According to the latest NPD Solarbuzz North America PV Markets Quarterly, demand for solar photovoltaic (PV) panels in the U.S. is forecast to grow significantly during 2013 and post another record high of 4.3 gigawats (GW). In addition, solar PV demand from the U.S. market now contributes over 12 percent of annual global demand compared to just five percent three years ago.
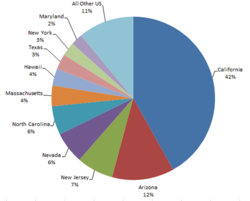
In second quarter 2013, demand is forecast to reach 1 GW with over 70 percent coming from California, Arizona, New Jersey and North Carolina. Residential and small commercial rooftop PV installations will account for 18 percent of this demand with another 14 percent from large commercial rooftops. The utility dominated ground mount segment will account for the remaining 68 percent.
 “The strong commercial and utility-based solar PV being deployed in the U.S. is stimulated by state specific mandates that require solar to meet target levels, or carve-outs, of total energy production,” explained Chris Sungon, analyst at NPD Solarbuzz. “Meanwhile residential demand is being driven by new third-party ownership models that allow homeowners and businesses to install PV systems with minimal upfront commitments.”
“The strong commercial and utility-based solar PV being deployed in the U.S. is stimulated by state specific mandates that require solar to meet target levels, or carve-outs, of total energy production,” explained Chris Sungon, analyst at NPD Solarbuzz. “Meanwhile residential demand is being driven by new third-party ownership models that allow homeowners and businesses to install PV systems with minimal upfront commitments.”
New solar PV incentive policies and additional utility-scale projects are also starting to diversify PV demand across a greater number of states within the US, moving away from the traditional strongholds limited to the East and West Coasts. Six of the 10 fastest-growing U.S. states for solar PV demand in 2013 are located in the South or the Midwest, providing annual growth rates averaging above 180 percent.Read More