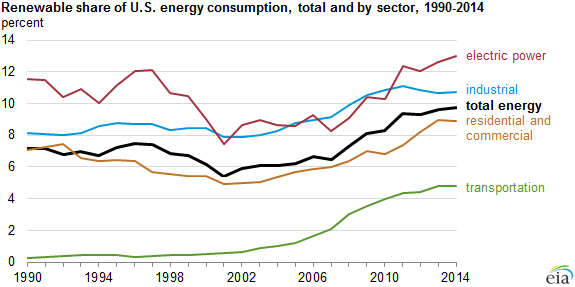
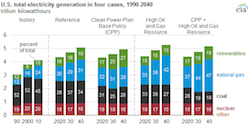
The biodiesel industry is relatively pleased with the announcement today from EPA setting volume requirements for biofuels under the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS).
 National Biodiesel Board (NBB) CEO Joe Jobe voiced “measured support” for the proposal while calling for improvements in the final rule.
National Biodiesel Board (NBB) CEO Joe Jobe voiced “measured support” for the proposal while calling for improvements in the final rule.
“It is not perfect, but it will get the U.S. biodiesel industry growing again and put people back to work,” said Jobe. “However, more can be done, and we particularly look forward to working with the administration on strengthening biodiesel volumes for 2016 and 2017 during the comment period in the coming weeks.”
Biodiesel falls under the Biomass-based Diesel category of the RFS, which is a subset of the overall Advanced Biofuels category. The EPA proposal, which is slated to be finalized in November, would gradually raise biodiesel volumes by about 100 million gallons per year to a standard of 1.9 billion gallons in 2017. Because of biodiesel’s higher energy content, this would count as 2.95 billion ethanol equivalent gallons under the RFS. The overall Advanced Biofuel standard would rise to 3.4 billion ethanol equivalent gallons in 2016. NBB had requested more aggressive growth to a biodiesel standard of 2.7 billion gallons by 2017, along with additional growth in the overall Advanced Biofuel category.