According to forecasts published in Biofuelscan, a daily report from Platts that covers the global biofuels industry, U.S. ethanol production data, to be reported on October 23, 2013 by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), ethanol production for the week ending October 18, 2013 was 861,000 barrels/day (b.d). This number would show an increase of 0.58 percent from last week’s Bentek Energy ethanol production forecast.
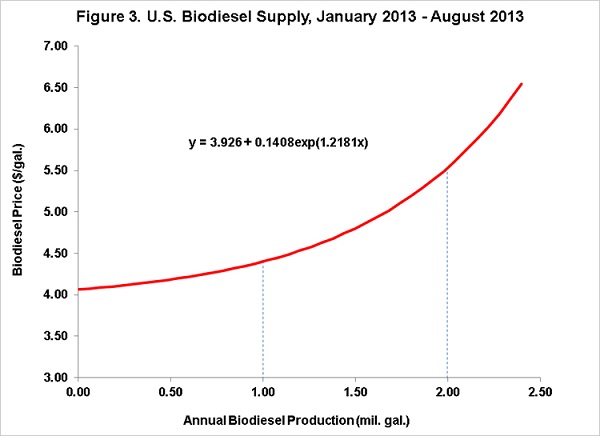
Corn futures prices have hovered near three-year lows and rising crush margins – the price difference between a gallon of ethanol and gallon of corn — have combined to boost ethanol production in recent weeks. As a result, ethanol production figure has risen for four of the past five weeks, and it is expected to rise further, given the projections of a bumper U.S. corn crop during the 2013 harvest season.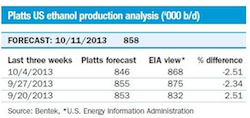
According to calculations from Kingsman, the sugar analytics unit of Platts, the crush margin will rise to 24.4 cents/gal for the reporting week, up 6.3 cents/gal from the prior week.
Platts began publishing its Bentek Energy and Kingsman forecasts of ethanol production and crush margins, respectively October 4, 2013 to fill a data gap during the temporary shutdown of the U.S. government related to lack of budget appropriations.
“We are pleased to meet a market need for independent estimates of this important government data series,” said Simon Thorne, editorial director of agriculture at Platts. “The advance forecasts are aimed at helping the marketplace better estimate price-sensitive data and assist customers in making better and timelier business decisions.”
The Bentek Energy forecast of U.S. ethanol production utilizes data from approximately the past three years and is calculated on actual consumption figures at ethanol production plants.
“When comparing the Bentek production forecast alongside the actual government production data, our estimate is within an average 0.06% – a very strong correlation since the records began in 2011,” concluded Thorne.